2 The first infrastructure - a virtual machine (EC2)
First of all we should create an AWS CDK project. You should already have the CDK command-line tool installed. If not, see the chapter about AWS CDK introduction and installation.
2.1 Our goals
First, let us clarify what we want to accomplish here:
- An EC2 instance
- The instance should run Linux, we will pick Amazon Linux 2023 for simplicity
- The instance should not be reachable from the internet
- We should be able to login and access the machine from a command-line prompt in the AWS Console.
- We should use an existing VPC and its subnets.
- We do not care about which availability zone the machine ends up in.
However, we will take smaller steps to reach this goal. Our first goal is simply to get an EC2 instance of any type up and running, in any VPC, subnet, availability zone - just get it up.
Let us see how we can accomplish these goals! We will run into some trouble on the way, which is intentional. There are a few hurdles and learnings to get started with AWS CDK. If you follow along, we should get through them one by one!
This chapter will be a bit long, since there are a few steps to get started with the AWS CDK. So hang in there, and we will get through all of these steps.
2.2 Initialize our project
Before writing any code, we should initialise our AWS CDK project to get started.
In a command-line shell, create a directory to contain the project, and go to that directory:
mkdir my-cdk-infrastructure
cd my-cdk-infrastructureWe can then run the command uv init to initialise the project. This will create 4 files at least: .python-version, hello.py, pyproject.toml, and README.md. This is all good for a regular uv project and we can run uv run hello.py to see that we can execute the code in hello.py.
❯ uv run hello.py
Hello from my-cdk-infrastructure!Under the hood, uv will install Python if it is not already available. It will also create a Python virtual environment if it is not already available, and run the code in that environment. Thus is is convenient to use uv run to execute the Python code instead of running the python interpreter directly.
However, this is not sufficient for the AWS CDK command-line tool. Thus, we have some additional work to get started with an AWS CDK project.
To test that our AWS CDK project looks ok, we will use the cdk command-line tool ands use the command cdk synth. It is a command to generate the CloudFormation from our CDK code:
❯ cdk synth
--app is required either in command-line, in cdk.json or in ~/.cdk.jsonThe cdkcommand-line tool needs to know how to run the code in the project, which can be done in many different ways. Normally, this is handled via a file cdk.json in the project directory, so we will add the minimum we need:
{
"app": "uv run hello.py"
}The “app” entry tells CDK how to run our code, which is the same as the command-line uv run hello.py. Run the cdk synth command again.
❯ cdk synth
Hello from my-cdk-infrastructure!
ENOENT: no such file or directory, open 'cdk.out/manifest.json'You will get an error after the code execution, which will be related to that we actually do not have any infrastructure defined at all. So this is fine to not worry about now, since it will go away when we start defining the infrastructure.
Now we are ready to start writing some infrastructure code!
2.3 Our first CDK code
Delete the hello.py file, and create a new file called first_infra.py. Open this file in a text editor of your choice. Also, in the file cdk.json rename the file name hello.pythere to first_infra.py.
In the AWS CDK introduction chapter, we covered some basic concepts of the AWS CDK, which include a CDK App. This is represented in Python as a class. We need to import it in the code, and create an object instance of that class:
import aws_cdk as cdk
app = cdk.App()
app.synth()The call to the synth() method will generate the CloudFormation template.
We also need to add this imported library as a dependency from PyPi:
uv add aws-cdk-libHowever, this is not sufficient.
❯ cdk synth
This app contains no stacks
❯ All AWS CDK application solutions need an App. It is not yet a useful piece of code that will produce anything we can deploy to AWS, as we can see, it also requires a stack to be defined.
The cdk synth command runs the Python code. The expected result is the CloudFormation that we can deploy to AWS. CloudFormation deploys stacks from templates, which we refer to as stacks in AWS CDK as well. So let us add a stack also, and associate that one with our App. AWS CDK has a Stack class for that purpose.
import aws_cdk as cdk
app = cdk.App()
stack = cdk.Stack(app, "my-stack");
app.synth()To create the stack, we specify two parameters - the AWS CDK app that the stack belongs to, and an identifier for the stack, which by default will be the name of the stack as well. This means that the name must be unique within an AWS account and region combination.
If your friends or colleagues share an AWS account, and do the same exercise, you should set your individual names to the stack! Otherwise things may get a bit messy if you would overwrite each others stacks…
If we run the cdk synth command again, we get some output:
❯ cdk synth
Resources:
CDKMetadata:
Type: AWS::CDK::Metadata
Properties:
Analytics: v2:deflate64:H4sIAAAAAAAA/zPSMzQ31DNUTCwv1k1OydbNyUzSqw4uSUzO1nFOywtKLc4vLUpOBbGd8/NSMksy8/NqdfLyU1L1sor1y4wM9AxBurOKMzN1i0rzSjJzU/WCIDQA1ab0kFoAAAA=
Metadata:
aws:cdk:path: my-stack/CDKMetadata/Default
Condition: CDKMetadataAvailable
Conditions:
CDKMetadataAvailable:
Fn::Or:
- Fn::Or:
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- af-south-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ap-east-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ap-northeast-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ap-northeast-2
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ap-northeast-3
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ap-south-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ap-south-2
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ap-southeast-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ap-southeast-2
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ap-southeast-3
- Fn::Or:
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ap-southeast-4
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ca-central-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- ca-west-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- cn-north-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- cn-northwest-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- eu-central-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- eu-central-2
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- eu-north-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- eu-south-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- eu-south-2
- Fn::Or:
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- eu-west-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- eu-west-2
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- eu-west-3
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- il-central-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- me-central-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- me-south-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- sa-east-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- us-east-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- us-east-2
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- us-west-1
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: AWS::Region
- us-west-2
Parameters:
BootstrapVersion:
Type: AWS::SSM::Parameter::Value<String>
Default: /cdk-bootstrap/hnb659fds/version
Description: Version of the CDK Bootstrap resources in this environment, automatically retrieved from SSM Parameter Store. [cdk:skip]
❯ Wohoo! We got some CloudFormation output!
This looks like a lot, but this is only some generic metadata essentially that the AWS CDK always includes. By default, the cdk synth command outputs the CloudFormation template that it has generated, if it is a single template. It can be a simple sanity check to see if what we have written might be something we can deploy, at least until we have unit tests, pipelines, etc in place.
In most cases, we do not want to see the CloudFormation template output though to do this check. We can avoid that by using the --quiet option:
❯ cdk synth --quiet
❯ Now we have a less verbose feedback loop here.
2.3.1 Create the EC2 instance
Ok, so we now have a foundation to actually deploy something to AWS, but we only have an empty stack, and we need to fill that with something - our EC2 instance.
The AWS CDK library has a number of submodules, one for each AWS service it supports (plus a few more). We want to use the aws-ec2 submodule. In that submodule we want to use the Instance class, that describes an EC2 instance resource.
We need to associate the instance with the stack we want to deploy, and we should give the instance a name as well. We use the same pattern as when we associated the stack with the AWS CDK App:
import aws_cdk as cdk
from aws_cdk import (
aws_ec2 as ec2
)
app = cdk.App()
stack = cdk.Stack(app, "my-stack")
instance = ec2.Instance(stack, "my-ec2")
app.synth()The name itself for the instance be an internal name in the AWS CDK App, it will not literally show up with the same name in AWS. The code above will not compile properly.
❯ cdk synth --quiet
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/eriklz/Documents/Dev/elz_repos/hands-on-iac-awscdk-code/python/first-infra/step1/first_infra.py", line 9, in <module>
instance = ec2.Instance(stack, 'my-ec2')
File "/Users/eriklz/Documents/Dev/elz_repos/hands-on-iac-awscdk-code/python/first-infra/step1/.venv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/jsii/_runtime.py", line 118, in __call__
inst = super(JSIIMeta, cast(JSIIMeta, cls)).__call__(*args, **kwargs)
TypeError: Instance.__init__() missing 3 required keyword-only arguments: 'instance_type', 'machine_image', and 'vpc'
Subprocess exited with error 1error: Uncaught (in promise) TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'initOptions')❯ cdk synth --quietMany resources will require additional parameters. In Python, you provide these as additional keyword parameters - these can be different for each type of resource.
To open up the AWS CDK documentation, you can use the command cdk docs. This command will open up a browser window/tab with the home page too the AWS CDK Api documentation. From there you can drill down to the aws_ec2 submodule, and in there find the Instance class. (Or use the link here)
In the documentation we can see that there are three things that must be specified, which was also reported in the error message we got:
- instance_type - the type of instance to launch
- machine_image - the Amazon Machine Image (AMI) to use
- vpc - the VPC to launch the EC2 instance in
We need to supply these three properties. Let us tackle them, one by one:
An instance type describes a combination of memory, CPU, disk and networking capacity for a virtual machine. AWS divides these into various families of virtual machines, and within each family there are multiple sizes of machines. For this setup we are going to go with an instance type which is part of the AWS free tier, which means if you have an AWS account that is less than 12 months, you should not need to pay anything for it. The family here is burstable compute generation 3, also known as T3 , and the size is micro. It a nice general purpose and small type of machine. In AWS CDK the instance family is also referred to as instance class. We can use the of() function for InstanceType to get the right instance type based on parameters we provide.
instance = ec2.Instance(
stack,
"my-ec2",
instance_type=ec2.InstanceType.of(ec2.InstanceClass.T3, ec2.InstanceSize.MICRO),
)Next, we should get the appropriate machine image to use. Since we do not care so much about specific versions at this point, we just want to get the latest Amazon Linux 2023 machine image. This is something AWS CDK can handle for us.
instance = ec2.Instance(
stack,
"my-ec2",
instance_type=ec2.InstanceType.of(ec2.InstanceClass.T3, ec2.InstanceSize.MICRO),
machine_image=ec2.MachineImage.latest_amazon_linux2023(),
)Last but not least, we need a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud - actually a network infrastructure) to launch the virtual machine into. We can create a new VPC or reuse an existing one. For simplicity, we are going to use the default VPC in the account. All AWS accounts have a default VPC, unless it has been explicitly removed. We assume for now that your account has a default VPC.
If you had been using CloudFormation, you would need to look for the default VPC in your account and note its VPC ID value, perhaps via AWS Console. In AWS CDK, we let the CDK itself do that work for us and do the lookup. We need to associate the lookup data with the stack we want to put the instance into also.
vpc = ec2.Vpc.from_lookup(stack, "my-vpc", is_default=True)This means that when the AWS CDK code runs, it will use the current AWS credentials to look up VPC information, based on criteria we specify. In this case, we just specify that we want the default VPC. We keep that in a variable named vpc, which we then pass in as property to our new instance.
vpc = ec2.Vpc.from_lookup(stack, "my-vpc", is_default=True)
instance = ec2.Instance(
stack,
"my-ec2",
instance_type=ec2.InstanceType.of(ec2.InstanceClass.T3, ec2.InstanceSize.MICRO),
machine_image=ec2.MachineImage.latest_amazon_linux2023(),
vpc=vpc,
)Now we have everything in place to create our EC2 instance it seems! Let us get it running!
2.3.2 Running the CDK code
To recap where we are, the complete code we have written so far looks like this, in Python:
import aws_cdk as cdk
from aws_cdk import aws_ec2 as ec2
app = cdk.App()
stack = cdk.Stack(app, "my-stack")
vpc = ec2.Vpc.from_lookup(stack, "my-vpc", is_default=True)
instance = ec2.Instance(
stack,
"my-ec2",
instance_type=ec2.InstanceType.of(ec2.InstanceClass.T3, ec2.InstanceSize.MICRO),
machine_image=ec2.MachineImage.latest_amazon_linux2023(),
)
app.synth()As we mentioned in the previous section, our code will look up the default VPC in the target account, based on the credentials we use, and it should create the EC2 instance in that VPC.
In the same way as we tested with the cdk synth command when we had an empty stack, we can test that again now and see if that works ok.
❯ cdk synth
jsii.errors.JavaScriptError:
@jsii/kernel.RuntimeError: Error: Cannot retrieve value from context provider vpc-provider since account/region are not specified at the stack level. Configure "env" with an account and region when you define your stack.See https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/latest/guide/environments.html for more details.Oops! What happened here? It could not generate the Cloudformation template for the stack. Also, what is this about JavaScript?
First, the error comes from the underlying implementation that is written in TypeScript (that in turn has been transpiled to JavaScript), which Python is talking to via something called JSII. So this error type is essentially a propagation of an error from the underlying TypeScript implementation.
The problem here is that we asked AWS CDK to look up the default VPC and include that in the generated CloudFormation. But to do that, it needs to know precisely which AWS account and region this stack is used for - it is not enough to implicitly assume whatever our current credentials refer to.
An optional parameter we can provide to the stack is the AWS environment, which includes the AWS account and the AWS region. With that information, the AWS CDK will be able to figure out exactly what VPC information to look up.
Luckily we do not need to hardcode this setting in the code, the CDK provides two environment variables that will be set for you, based on current AWS credentials and settings. These environment variables are:
- CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT
- CDK_DEFAULT_REGION
The CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT environment variable contains the current AWS account ID, e.g. 123456789012. The CDK_DEFAULT_REGION will reflect what region setting is current, e.g. eu-north-1. We change the stack creation slightly to include these settings
environment = cdk.Environment(
account=os.getenv("CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT"), region=os.getenv("CDK_DEFAULT_REGION")
)
stack = cdk.Stack(app, "my-stack", env=environment)We also want to add an import for os:
import osUp to this point, we have been able to run cdk synth without using any AWS credentials. But now we need to tell AWS CDK to use the current AWS credentials to look up the VPC information. So you should from now on make sure that you have valid AWS credentials active from the command-line you are running. If you have an AWS profile configured, you can set the environment variable AWS_PROFILE to that profile name.
Now, when we run cdk synth again, we will get a different output:
❯ cdk synth
Resources:
myec2InstanceSecurityGroup1CDE1A58:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupDescription: my-stack/my-ec2/InstanceSecurityGroup
.. more CloudFormation output ..If you looked at the generated output from cdk synth, you would see that the VPC Id of the default VPC in your AWS account is in fact in place. You can also see it in a new file in the directory of your project, which name is cdk.context.json. If you look in this file, you will se references to VPC Id, subnets, route tables , etc.
All that is data that has been saved in this file when AWS CDK performed the lookup. This file acts as a cache for various data from the environments you work with. Any data that AWS CDK tries to look up, it will fetch from this file rather than the actual AWS environment, if it is present.
This approach to handle existing data in the environment is part of an approach to make predictable deployments in AWS CDK, which we get into more depth later.
2.3.3 Deploy the EC2 instance
So can we finally deploy that EC2 instance? Yes, maybe! Let us run the cdk deploy command
❯ cdk deploy
current credentials could not be used to assume 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/cdk-hnb659fds-lookup-role-123456789012-eu-west-1', but are for the right account. Proceeding anyway.
✨ Synthesis time: 2.31s
current credentials could not be used to assume 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/cdk-hnb659fds-deploy-role-123456789012-eu-west-1', but are for the right account. Proceeding anyway.
my-stack: SSM parameter /cdk-bootstrap/hnb659fds/version not found. Has the environment been bootstrapped? Please run 'cdk bootstrap' (see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/latest/guide/bootstrapping.html)Sigh… Why is it failing now? The error message tells us what the problem likely is - we have not bootstrapped the environment!
What is bootstrapping, and why do we need to do that?
For AWS CDK, bootstrapping is preparing each AWS environment (AWS account + region combination) for deployments. That includes setting up S3 bucket for deployment, set IAM roles to use with single- or multi-account or region deployments, and lookups.
This bootstrapping process is something that you normally do once per account + region combination. To perform a simple single account bootstrap, we just run cdk bootstrap. This will deploy a CloudFormation stack with the name CDKToolkit. You can see the progress of the bootstrap when the command executes.
❯ cdk bootstrap
⏳ Bootstrapping environment aws://123456789012/eu-west-1...
Trusted accounts for deployment: (none)
Trusted accounts for lookup: (none)
Using default execution policy of 'arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess'. Pass '--cloudformation-execution-policies' to customize.
CDKToolkit: creating CloudFormation changeset...
✅ Environment aws://123456789012/eu-west-1 bootstrapped.Now, if we run cdk deploy again we get a different output:
❯ cdk deploy
✨ Synthesis time: 3.13s
my-stack: start: Building 5c3ebcfeea7bbc9d08bd8ed5e6d5aa522fb2c77e8eaf7a5bbfa8b66e077fff37:123456789012-eu-west-1
my-stack: success: Built 5c3ebcfeea7bbc9d08bd8ed5e6d5aa522fb2c77e8eaf7a5bbfa8b66e077fff37:123456789012-eu-west-1
my-stack: start: Publishing 5c3ebcfeea7bbc9d08bd8ed5e6d5aa522fb2c77e8eaf7a5bbfa8b66e077fff37:123456789012-eu-west-1
my-stack: success: Published 5c3ebcfeea7bbc9d08bd8ed5e6d5aa522fb2c77e8eaf7a5bbfa8b66e077fff37:123456789012-eu-west-1
Stack undefined
This deployment will make potentially sensitive changes according to your current security approval level (--require-approval broadening).
Please confirm you intend to make the following modifications:
IAM Statement Changes
┌───┬────────────────────────────┬────────┬────────────────┬───────────────────────────┬───────────┐
│ │ Resource │ Effect │ Action │ Principal │ Condition │
├───┼────────────────────────────┼────────┼────────────────┼───────────────────────────┼───────────┤
│ + │ ${my-ec2/InstanceRole.Arn} │ Allow │ sts:AssumeRole │ Service:ec2.amazonaws.com │ │
└───┴────────────────────────────┴────────┴────────────────┴───────────────────────────┴───────────┘
Security Group Changes
┌───┬─────────────────────────────────────────┬─────┬────────────┬─────────────────┐
│ │ Group │ Dir │ Protocol │ Peer │
├───┼─────────────────────────────────────────┼─────┼────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ + │ ${my-ec2/InstanceSecurityGroup.GroupId} │ Out │ Everything │ Everyone (IPv4) │
└───┴─────────────────────────────────────────┴─────┴────────────┴─────────────────┘
(NOTE: There may be security-related changes not in this list. See https://github.com/aws/aws-cdk/issues/1299)What is this question and what is the data shown here? The AWS CDK has a safety check, if your deployment will perform changes that adds permissions in some way, it will be default ask if you are really sure about this. In this case, we are ok with outbound traffic from the EC2 instance role, which is the security group part. There is no inbound communication open to the EC2 instance, at all. For the IAM permissions, there is right now only a dummy change - it will be possible to assign IAM permissions to this EC2 instance, but we have not added any yet.
So it is safe for us to answer yes here and continue.
Do you wish to deploy these changes (y/n)? y
my-stack: deploying... [1/1]
my-stack: creating CloudFormation changeset...
✅ my-stack
✨ Deployment time: 175.01s
Stack ARN:
arn:aws:cloudformation:eu-west-1:123456789012:stack/my-stack/1228c5e0-b3b1-11ef-b900-06761dbb511f
✨ Total time: 178.14sNow that looks a bit better! Similar to the bootstrap process, AWS CDK reports the progress of the deployment in the command-line interface.
If we take a look in the AWS Console under EC2, we might see something like this:
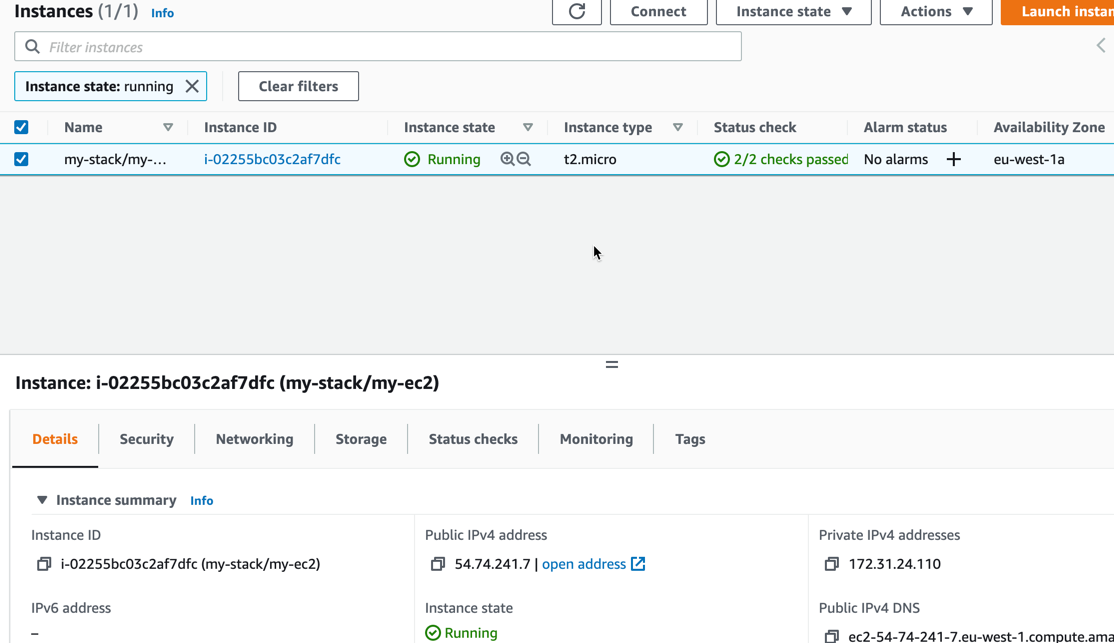
We have an instance running, and that is great!
However, it does have a public IP address, but we did not want it to be reachable from internet. We do have a security group associated with the instance that does not allow any inbound traffic, so it is still blocked from traffic, despite the public IP address.
But, how are we going to login to the machine and still block public access? This will be what we cover in the next chapter, which will be shorter than this one.
For now, we will clean up after ourselves and delete this instance, and all associated resources that we created with it. We can do that easily with the cdk destroy command.
❯ cdk destroy
Are you sure you want to delete: my-stack (y/n)? y
my-stack: destroying...
✅ my-stack: destroyedThis is a good habit if you are going to take a break right now (you deserve it!) before you continue. Since you have it all in code, you can just run cdk deploy again later to re-create what you have done so far.